Zeppelin Ransomware

Technical Details
Note: this advisory uses the MITRE ATT&CK® for Enterprise framework, version 11. See MITRE ATT&CK for Enterprise for all referenced tactics and techniques.
Zeppelin ransomware is a derivative of the Delphi-based Vega malware family and functions as a Ransomware as a Service (RaaS). From 2019 through at least June 2022, actors have used this malware to target a wide range of businesses and critical infrastructure organizations, including defense contractors, educational institutions, manufacturers, technology companies, and especially organizations in the healthcare and medical industries. Zeppelin actors have been known to request ransom payments in Bitcoin, with initial amounts ranging from several thousand dollars to over a million dollars.
Zeppelin actors gain access to victim networks via RDP exploitation [T1133], exploiting SonicWall firewall vulnerabilities [T1190], and phishing campaigns [T1566]. Prior to deploying Zeppelin ransomware, actors spend one to two weeks mapping or enumerating the victim network to identify data enclaves, including cloud storage and network backups [TA0007]. Zeppelin actors can deploy Zeppelin ransomware as a .dll or .exe file or contained within a PowerShell loader. [1]
Prior to encryption, Zeppelin actors exfiltrate [TA0010] sensitive company data files to sell or publish in the event the victim refuses to pay the ransom. Once the ransomware is executed, a randomized nine-digit hexadecimal number is appended to each encrypted file as a file extension, e.g., file.txt.txt.C59-E0C-929 [T1486]. A note file with a ransom note is left on compromised systems, frequently on the desktop (see figure 1 below).
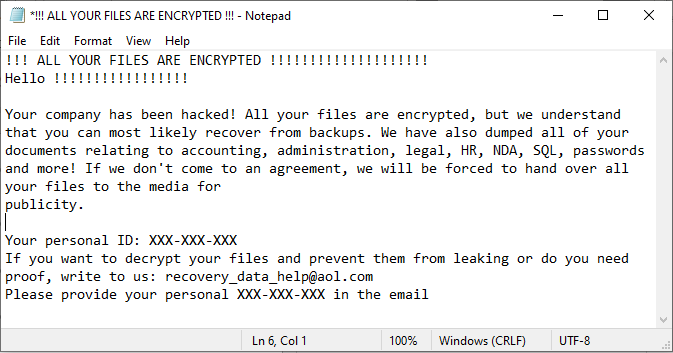
The FBI has observed instances where Zeppelin actors executed their malware multiple times within a victim’s network, resulting in the creation of different IDs or file extensions, for each instance of an attack; this results in the victim needing several unique decryption keys.
Indicators of Compromise (IOC)
See table 1 below for IOCs as of June 2022 obtained from FBI incident response investigations.
| MD5 | SHA1 | SHA256 |
| 981526650af8d6f8f20177a26abb513a | 4fee2cb5c98abbe556e9c7ccfebe9df4f8cde53f | 001938ed01bfde6b100927ff8199c65d1bff30381b80b846f2e3fe5a0d2df21d |
| c25d45e9bbfea29cb6d9ee0d9bf2864d | eaeff8d315cca71e997063a2baec5cc73fad9453 | a42185d506e08160cb96c81801fbe173fb071f4a2f284830580541e057f4423b |
| 183b6b0c90c1e0276a2015752344a4cf | 1cb5e8132302b420af9b1e5f333c507d8b2a2441 | aa7e2d63fc991990958dfb795a0aed254149f185f403231eaebe35147f4b5ebe |
| 9349e1cc3de7c7f6893a21bd6c3c4a6b | db398e38ee6221df7e4aa49d8f96799cca4d87e1 | a2a9385cbbcfacc2d541f5bd92c38b0376b15002901b2fd1cc62859e161a8037 |
| c8f75487d0d496a3746e6c81a5ecc6dc | 4b91a91a98a2f0128c80f8ceeef0f5d293adf0cd | 54d567812eca7fc5f2ff566e7fb8a93618b6d2357ce71776238e0b94d55172b1 |
| 477eedb422041385e59a4fff72cb97c1 | 9892cc90e6712d3548e45f34f14f362bccedf0be | fb59f163a2372d09cd0fc75341d3972fdd3087d2d507961303656b1d791b17c6 |
| 5841ef35aaff08bb03d25e5afe3856a2 | ffd228b0d7afe7cab4e9734f7093e7ba01c5a06e | 1e3c5a0aa079f8dfcc49cdca82891ab78d016a919d9810120b79c5deb332f388 |
| d6c4b253ab1d169cf312fec12cc9a28f | 0f47c279fea1423c7a0e7bc967d9ff3fae7a0de8 | 347f14497df4df73bc414f4e852c5490b12db991a4b3811712bac7476a3f1bc9 |
| fba7180ad49d6a7f3c60c890e2784704 | f561f9e3c949fe87f12dbfa166ffb2eb85712419 | 7d8c4c742689c097ac861fcbf7734709fd7dcab1f7ef2ceffb4b0b7dec109f55 |
| bc6c991941d9afbd522fa0a2a248a97a | a243ce234fc8294e2e2e526418b4eaadc2d6c84f | 37c320983ae4c1fd0897736a53e5b0481edb1d1d91b366f047aa024b0fc0a86e |
| f3490951ae51922cb360a3d76a670159 | e2cb60be111716e32db7ca2365ad6e73c30f0e21 | 894b03ed203cfa712a28ec472efec0ca9a55d6058115970fe7d1697a3ddb0072 |
| e4f1f05c2e6c3fc2f3336a8c8799ffb4 | dbd9fcf2b05e703d34181c46f4c22392b9fcc1da | 307877881957a297e41d75c84e9a965f1cd07ac9d026314dcaff55c4da23d03e |
| aa2048271f0aef3383480ce4a7c93b52 | 512b16ea74027fa4d0055831de5e51278812c8de | bafd3434f3ba5bb9685e239762281d4c7504de7e0cfd9d6394e4a85b4882ff5d |
| f66b738e1bfe1f8aab510abed850c424 | 571f50fee0acad1da39fe06c75116461800cc719 | faa79c796c27b11c4f007023e50509662eac4bca99a71b26a9122c260abfb3c6 |
| bb30f050546f5d6e61fafc59eaf097c3 | ee44179f64918f72a8d2e88a5074d89efab3d81b | e48cf17caffc40815efb907e522475722f059990afc19ac516592231a783e878 |
| 78621f1e196497d440afb57f4609fcf9 | eed7c3bb3fc5181b88abeed2204997f350324022 | 4a4be110d587421ad50d2b1a38b108fa05f314631066a2e96a1c85cc05814080 |
| f4e0ee0200de397691748a2cdcd7e34a | bd3f6b878284a63c72e8354e877e3f48d6fca53c | 9ef90ec912543cc24e18e73299296f14cb2c931a5d633d4c097efa372ae59846 |
| cf5a358a22326f09fd55983bb812b7d8 | 1addcffae4fd4211ea24202783c2ffad6771aa34 | dd89d939c941a53d6188232288a3bd73ba9baf0b4ca6bf6ccca697d9ee42533f |
| 7afe492a38ca6f27e24028aab68406b5 | 5870a3adbce9737319f3c9461586d5f2afbc7adb | 79d6e498e7789aaccd8caa610e8c15836267c6a668c322111708cf80bc38286c |
| 1da1c0115caca5ebf064380eb7490041 | 5edb8b651c7013ebaba2eb81c87df76a1e0724d6 | b22b3625bcce7b010c0ee621434878c5f8d7691c2a101ae248dd221a70668ac0 |
| 8c3c663ffcf363d087f4e114a79945ca | 905726d178962dd1d7fe87504d051aca440740b8 | 961fbc7641f04f9fed8391c387f01d64435dda6af1164be58c4cb808b08cc910 |
| 17c5cae3bce5832dd42986fe612517d9 | 6f70e73c53d7622d8c4808ae7849133df1343484 | d618c1ccd24d29e911cd3e899a4df2625155297e80f4c5c1354bc2e79f70768c |
| bfe7f54f1f0640936dd7a3384608b1f6 | 9436ccee41c01ca3cb4db55c10884615aba76d19 | 8170612574f914eec9e66902767b834432a75b1d6ae510f77546af2a291a48a2 |
| f28af04ef0370addfebfdd31f1ec25ed | cfcfa995c15d9f33de21d0dd88d3b95d0f91d6bc | 5326f52bd9a7a52759fe2fde3407dc28e8c2caa33abf1c09c47b192a1c004c12 |
| f3bcad5358f89df1eb0294ef53f54437 | eb036759beb28f86ee981bdca4fad24152b82d8c | 6bafc7e2c7edc2167db187f50106e57b49d4a0e1b9269f1d8a40f824f2ccb42b |
| b1f6370582fbaf5c51e826fecef53cd7 | 4b2d0127699f708a8116bff8f25c9d6140033197 | f7af51f1b2b98b482885b702508bd65d310108a506e6d8cef3986e69f972c67d |
| de785ed922d4e737dc0fa0bb30a4de8b | 4d280105e724db851f03de8fc76409ef4057ff2c | bc214c74bdf6f6781f0de994750ba3c50c0e10d9db3483183bd47f5cef154509 |
| 7a296f7c1ac4aeee18d4c23476735be7 | c13542310f7a4e50a78247fc7334096ca09c5d7f | ed1548744db512a5502474116828f75737aec8bb11133d5e4ad44be16aa3666b |
| 37f18b38e1af6533d93bbb3f2ddb86dc | d3929331d9bc278dea5607aec1574012a08de861 | cf9b6dda84cbf2dbfc6edd7a740f50bddc128842565c590d8126e5d93c024ff2 |
| 291de974e5cbe5e3d47e3d17487e027f | def93f18aaf146fe8f3c4f9a257364f181197608 | 21807d9fcaa91a0945e80d92778760e7856268883d36139a1ad29ab91f9d983d |
| 99d59c862a082b207a868e409ce2d97c | 908a9026d61717b5fa29959478a9bd939da9206f | 0d22d3d637930e7c26a0f16513ec438243a8a01ea9c9d856acbcda61fcb7b499 |
| d27125d534e398f1873b7f4835a79f09 | 1862f063c30cd02cfea6070d3dba41ac5eee2a35 | 6fbfc8319ed7996761b613c18c8cb6b92a1eaed1555dae6c6b8e2594ac5fa2b9 |
| 4534f2afe5f7df1d998f37ad4e35afeb | e2cc94e471509f9fa58620b8bb56d77f2cfe74b0 | e8596675fef4ad8378e4220c22f4358fdb4a20531b59d7df5382c421867520a9 |
| 7ab0676262c681b8ec15bdada17d7476 | 2f1803d444891abb604864d476a8feac0d614f77 | 353e59e96cbf6ea6c16d06da5579d3815aaaeeefacabd7b35ba31f7b17207c5b |
| d7d3d23a5e796be844af443bda5cd67e | a9771c591f6ccc2f3419d571c64ab93228785771 | 85f9bf4d07bc2ac1891e367f077dd513d6ca07705bffd1b648d32a7b2dc396f5 |
| 0a1cd4efda7543cec406a6822418daf6 | af4f8d889d6a2049e7a379ea197f8cd361feb074 | 614cb70659ef5bb2f641f09785adc4ab5873e0564a5303252d3c141a899253b2 |
| 23eda650479fc4908d0ddff713508025 | b1e6527c10f68586f7f1a279ed439d46c3f12a06 | fb3e0f1e6f53ffe680d66d2143f06eb6363897d374dc5dc63eb2f28188b8ad83 |
| 6607d8c1a28d7538e2a6565cf40d1260 | f618879c011cde344066072949f025827feea663 | 594df9c402abfdc3c838d871c3395ac047f256b2ac2fd6ff66b371252978348d |
| caa7a669da39ffd8a3a4f3419018b363 | 44538b7f8f065e3cef0049089a8522a76a7fccc6 | 2dffe3ba5c70af51ddf0ff5a322eba0746f3bf3ae0751beb3dc0059ed3faaf3d |
| 48b844494a746ca96c7b96d6bd90f45f | 7bf83b98f798f3a8f4ce85b6d29554a435e516e3 | 45fba1ef399f41227ae4d14228253237b5eb464f56cab92c91a6a964dc790622 |
| 9c13ab7b79aec8dc02869999773cd4b2 | 4b4d865132329e0dd1d129e85fc4fa9ad0c1d206 | 774ef04333c3fb2a6a4407654e28c2900c62bd202ad6e5909336eb9bc180d279 |
| 450e5bf4b42691924d09267ac1a570cb | 665a563157f4aa0033a15c88f55ac4fa28397b49 | 677035259ba8342f1a624fd09168c42017bdca9ebc0b39bf6c37852899331460 |
| 51104215a618a5f56ad9c884d6832f79 | 801580a46f9759ceeeebbce419d879e2ed6943fe | 26ec12b63c0e4e60d839aea592c4b5dcff853589b53626e1dbf8c656f4ee6c64 |
| 73627cbe2ba139e2ec26889a4e8d6284 | 1116dc35993fce8118e1e5421000a70b6777433f | 37efe10b04090995e2f3d9f932c3653b27a65fc76811fa583934a725d41a6b08 |
| 935f54b6609c5339001579e96dc34244 | a809327d39fab61bfcfac0c97b1d4b3bfb9a2cfe | a5847867730e7849117c31cdae8bb0a25004635d49f366fbfaebce034d865d7d |
| ba681db97f283c2e784d9bb4969b1f5a | 5d28acf52f399793e82ec7e79da47d372d9175d7 | e61edbddf9aed8a52e9be1165a0440f1b6e9943ae634148df0d0517a0cf2db13 |
| c1ab7b68262b5ab31c45327e7138fd25 | b8c74327831e460d2b2a8eb7e68ee68938779d8d | 746f0c02c832b079aec221c04d2a4eb790287f6d10d39b95595a7df4086f457f |
| f818938b987236cdd41195796b4c1fb5 | bfed40f050175935277c802cbbbce132f44c06ec | b191a004b6d8a706aba82a2d1052bcb7bed0c286a0a6e4e0c4723f073af52e7c |
| 0a1cd4efda7543cec406a6822418daf6 | af4f8d889d6a2049e7a379ea197f8cd361feb074 | 614cb70659ef5bb2f641f09785adc4ab5873e0564a5303252d3c141a899253b2 |
| d7d3d23a5e796be844af443bda5cd67e | a9771c591f6ccc2f3419d571c64ab93228785771 | 85f9bf4d07bc2ac1891e367f077dd513d6ca07705bffd1b648d32a7b2dc396f5 |
| 7ab0676262c681b8ec15bdada17d7476 | 2f1803d444891abb604864d476a8feac0d614f77 | 353e59e96cbf6ea6c16d06da5579d3815aaaeeefacabd7b35ba31f7b17207c5b |
| 4534f2afe5f7df1d998f37ad4e35afeb | e2cc94e471509f9fa58620b8bb56d77f2cfe74b0 | e8596675fef4ad8378e4220c22f4358fdb4a20531b59d7df5382c421867520a9 |
| d27125d534e398f1873b7f4835a79f09 | 1862f063c30cd02cfea6070d3dba41ac5eee2a35 | 6fbfc8319ed7996761b613c18c8cb6b92a1eaed1555dae6c6b8e2594ac5fa2b9 |
| 99d59c862a082b207a868e409ce2d97c | 908a9026d61717b5fa29959478a9bd939da9206f | 0d22d3d637930e7c26a0f16513ec438243a8a01ea9c9d856acbcda61fcb7b499 |
Download the YARA signature for Zeppelin: YARA Signature, .yar 125 kb
Mitigations
The FBI and CISA recommend network defenders apply the following mitigations to limit potential adversarial use of common system and network discovery techniques and to reduce the risk of compromise by Zeppelin ransomware:
Implement a recovery plan to maintain and retain multiple copies of sensitive or proprietary data and servers in a physically separate, segmented, and secure location (i.e., hard drive, storage device, the cloud).
Require all accounts with password logins (e.g., service account, admin accounts, and domain admin accounts) to comply with National Institute for Standards and Technology (NIST) standards for developing and managing password policies.Use longer passwords consisting of at least 8 characters and no more than 64 characters in length;
Store passwords in hashed format using industry-recognized password managers;
Add password user “salts” to shared login credentials;
Avoid reusing passwords;
Implement multiple failed login attempt account lockouts;
Disable password “hints”;
Refrain from requiring password changes more frequently than once per year. Note: NIST guidance suggests favoring longer passwords instead of requiring regular and frequent password resets. Frequent password resets are more likely to result in users developing password “patterns” cyber criminals can easily decipher.
Require administrator credentials to install software.
Require multifactor authentication for all services to the extent possible, particularly for webmail, virtual private networks, and accounts that access critical systems.
Keep all operating systems, software, and firmware up to date. Timely patching is one of the most efficient and cost-effective steps an organization can take to minimize its exposure to cybersecurity threats. Prioritize patching SonicWall firewall vulnerabilities and known exploited vulnerabilities in internet-facing systems. Note: SonicWall maintains a vulnerability list that includes Advisory ID, CVE, and mitigation. Their list can be found at psirt.global.sonicwall.com/vuln-list
.
Segment networks to prevent the spread of ransomware. Network segmentation can help prevent the spread of ransomware by controlling traffic flows between—and access to—various subnetworks and by restricting adversary lateral movement.
Identify, detect, and investigate abnormal activity and potential traversal of the indicated ransomware with a networking monitoring tool. To aid in detecting the ransomware, implement a tool that logs and reports all network traffic, including lateral movement activity on a network. Endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools are particularly useful for detecting lateral connections as they have insight into common and uncommon network connections for each host.
Install, regularly update, and enable real time detection for antivirus software on all hosts.
Review domain controllers, servers, workstations, and active directories for new and/or unrecognized accounts.
Audit user accounts with administrative privileges and configure access controls according to the principle of least privilege.
Disable unused ports.
Consider adding an email banner to emails received from outside your organization.
Disable hyperlinks in received emails.
Implement time-based access for accounts set at the admin level and higher. For example, the Just-in-Time (JIT) access method provisions privileged access when needed and can support enforcement of the principle of least privilege (as well as the Zero Trust model). This is a process where a network-wide policy is set in place to automatically disable admin accounts at the Active Directory level when the account is not in direct need. Individual users may submit their requests through an automated process that grants them access to a specified system for a set timeframe when they need to support the completion of a certain task.
Disable command-line and scripting activities and permissions. Privilege escalation and lateral movement often depend on software utilities running from the command line. If threat actors are not able to run these tools, they will have difficulty escalating privileges and/or moving laterally.
Maintain offline backups of data, and regularly maintain backup and restoration. By instituting this practice, the organization ensures they will not be severely interrupted, and/or only have irretrievable data.
Ensure all backup data is encrypted, immutable (i.e., cannot be altered or deleted), and covers the entire organization’s data infrastructure.
RESOURCES
Stopransomware.gov is a whole-of-government approach that gives one central location for ransomware resources and alerts.
Resource to mitigate a ransomware attack: CISA-Multi-State Information Sharing and Analysis Center (MS-ISAC) Joint Ransomware Guide.
No-cost cyber hygiene services: Cyber Hygiene Services and Ransomware Readiness Assessment
.










